Diseases of superficial veins
You can see the different stages of vein diseases below. In the respective section, you can find out more about the anatomical explanation of the disease, the disease itself, its symptoms, possible prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation.
Please note that the symptoms may be combined. An accurate diagnosis can be made if you consult a phlebologist and undergo a duplex ultrasound.
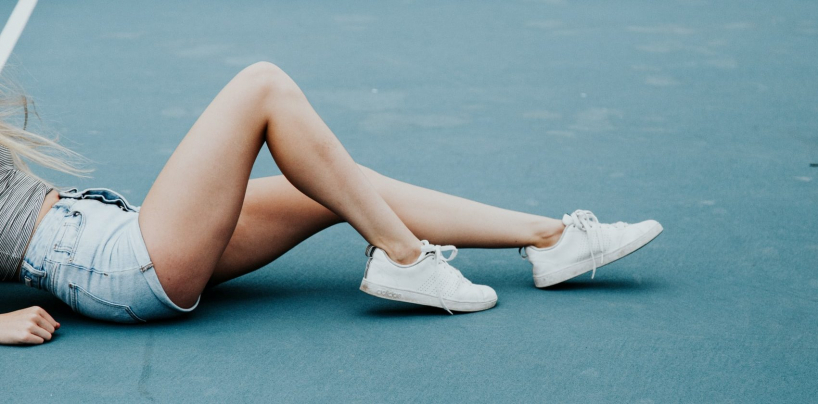
Superficial vein insufficiency is the cause of different degrees of varicose veins
THE VEINS ARE DIVIDED INTO GROUPS DEPENDING ON THEIR LOCALISATION AND DIAMETER:
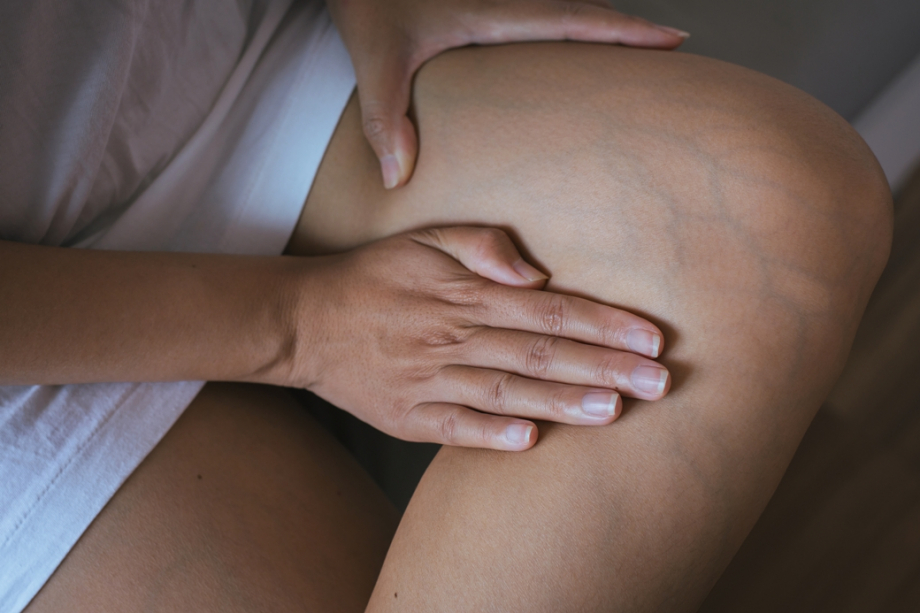
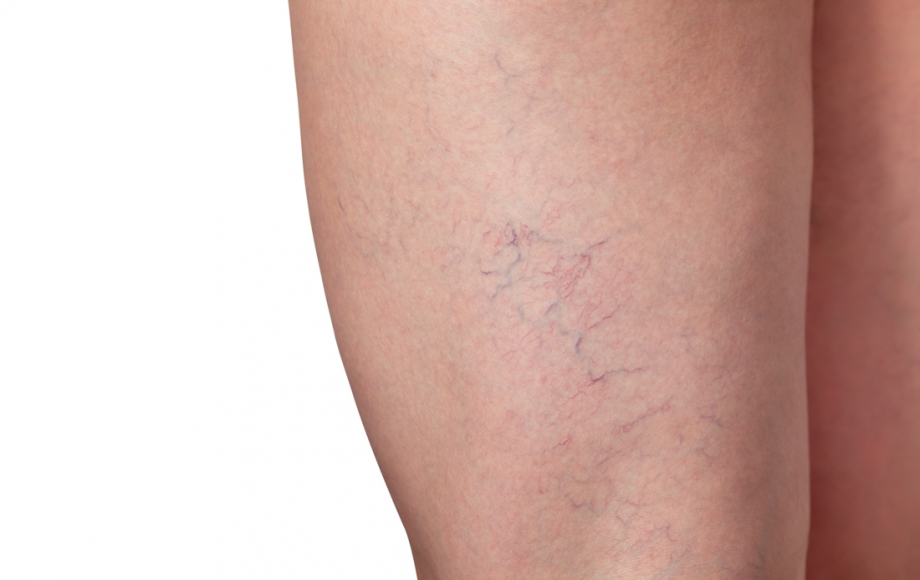
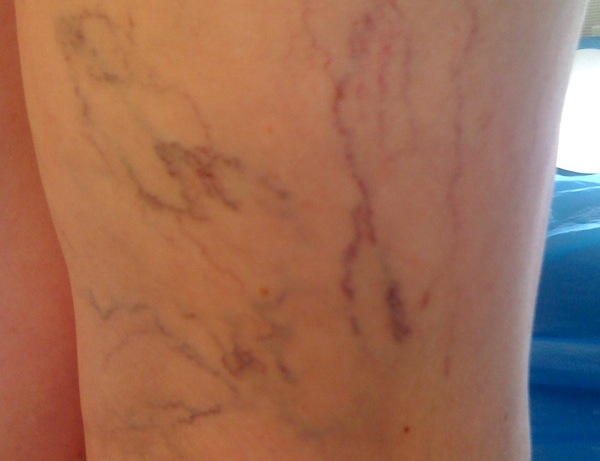
Telangiectasias
Spider veins (<1.0 mm in diameter) are caused by venous hypertension when the intradermal capillary veins dilate. Their appearance can sometimes suggest changes in the deep vein system. However, it is the cosmetic defect that concerns most patients.
Reticular veins
Their diameter is < 3.0 mm. Reticular veins are located in the hypodermis and their dilatation is not clinically significant but causes a visual defect.
Trunk veins and their main branches
Their diameter is > 3.0 mm; in case of abnormality, they cause both clinically and cosmetically significant changes with significant varicose veins, sensation of heaviness, itching, impaired skin trophism.
Lateral branches
They branch off from the trunk vein. Varicose changes in the lateral branches occur when the wall of a blood vessel unevenly dilates, and blood counter-flow occurs. This results in impaired venous outflow.
Perforator veins
Damage to the valves of this vein causes venous reflux from the deep vein system to the superficial veins. Insufficiency of isolated perforator veins is sometimes observed. Damage to the perforator veins in the lower legs often causes venous atrophic ulceration.
VARICOSE CAPILLARIES OR TELANGIECTASIAS
They appear as small, dilated blue veins or spider veins. They are often mistaken for a 'bruise'.
Telangiectasias (<1.0 mm in diameter), (capillary network, spider veins) are formed when the venous hypertension causes the intradermal capillary veins to dilate. Their appearance can sometimes suggest changes in the deep vein system. However, it is the cosmetic defect that concerns most patients.
Reticular veins (< 3.0 mm in diameter) are located in the hypodermis and their dilatation has no clinical significance, but like the reticular veins, they cause visual defects.
HOW DANGEROUS IT IS?
They are not clinically dangerous and cause only cosmetic defects. They appear more in women as they grow older. They are rather rare in men. Consultation with a phlebologist is highly recommended. Can be treated by sclerotherapy or laser procedures. Hormonal contraception or HRT is not recommended.
TREATMENT:
- sclerotherapy,
- laser therapy,
- thermocoagulation,
- drugs.
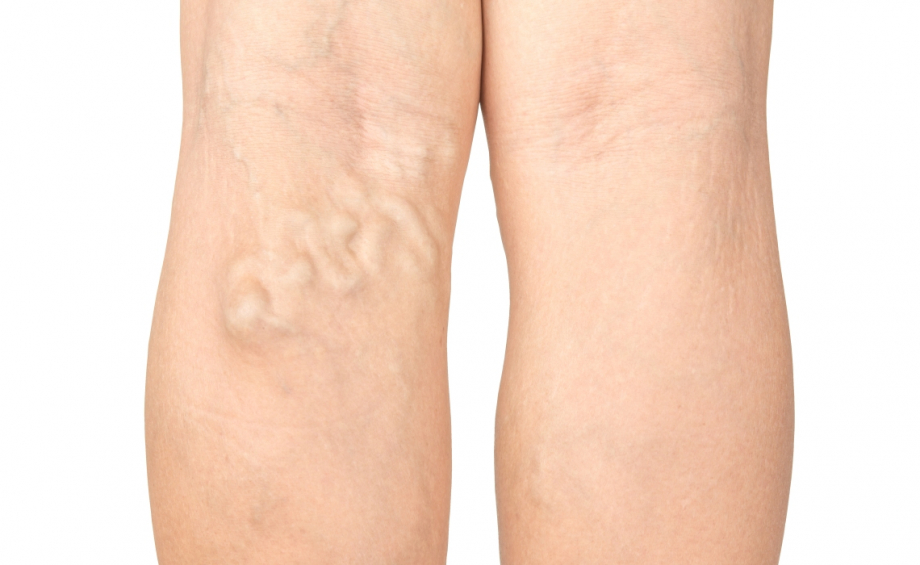
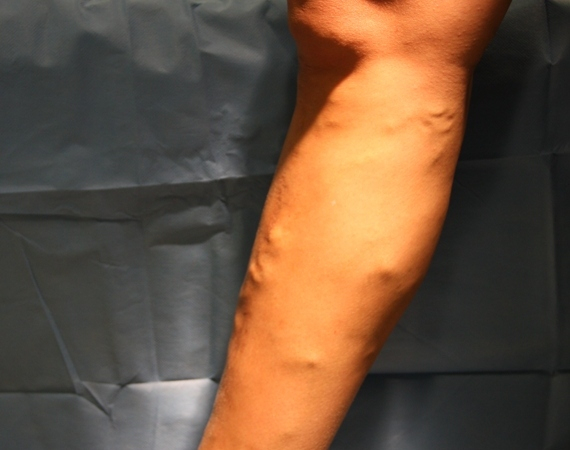
VENOUS NODES
Varicose veins are usually the first symptom noticed by the patient. The cause of varicose or dilated veins is damage to the valves of trunk veins VSM and VSP.
In case of abnormality of trunk veins and their main branches (>3.0 mm in diameter) they cause both clinically and cosmetically significant changes with significant varicose veins, sensation of heaviness, itching, impaired skin trophism.
We recommend consulting a phlebologist in case of venous nodes. A duplex ultrasound scan of the leg veins is required.
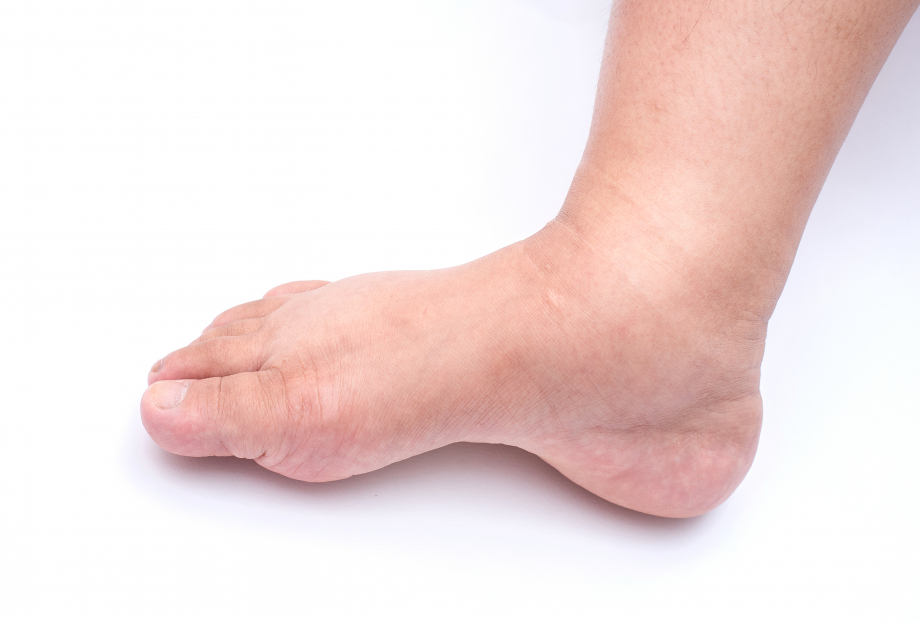
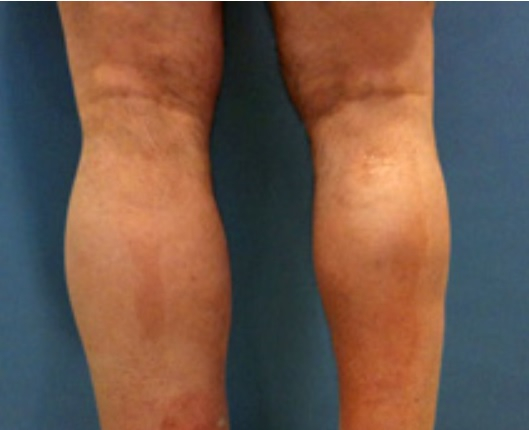
SWELLING OF THE LEGS
Swelling of the legs, just like varicose vein nodes, is usually the first symptom noticed by the patient. The cause of varicose or dilated veins is damage to the valves of trunk veins VSM and VSP.
In case of abnormality of trunk veins and their main branches (>3.0 mm in diameter) they cause both clinically and cosmetically significant changes with significant varicose veins, sensation of heaviness, itching, impaired skin trophism.
A consultation of a phlebologist is necessary. Undergo a duplex ultrasound scan of the leg veins. First, eliminate the venous reflux of the damaged trunk vein and only then remove the varicose nodes, not the other way round.
TREATMENT
In case of oedema, diagnosis is important to identify the cause of the swelling:
- venous insufficiency,
- lymphostasis,
- cardiac insufficiency,
- obesity,
- other cause.
The underlying disease is treated to reduce the swelling.
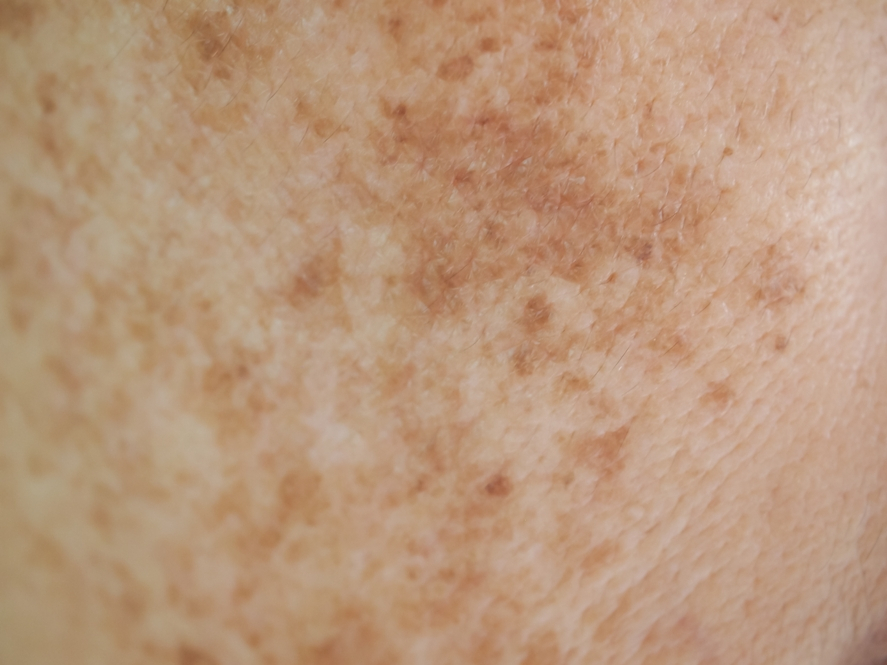
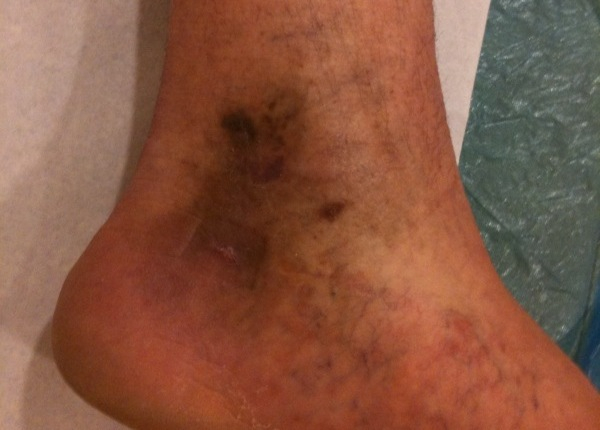
PIGMENTATION
Brownish-red spots usually appear on the inside of the lower legs. They are associated with prolonged venous stasis but can be a symptom accompanying other conditions.
Be sure to consult a phlebologist, dermatologist, or specialist in laser therapy. Pigmentation should be taken extremely seriously, and action should be taken as soon as possible, as it can be associated with serious problem of deep veins which, if not treated, can lead to incurable vein damage with extremely unpleasant consequences for the rest of your life.
The underlying cause of pigmentation is often neglected for an unreasonably long time, as we are used to freckles, haematomas (bruises) and other visual changes of the skin, attributing them to everyday micro-injuries. Be careful, observe and take care of yourself. Consult a doctor if you have any suspicions.
TREATMENT
In case of pigmentation, diagnosis is important to establish the cause of the pigmentation and eliminate it. Pigmentation can suggest extremely severe vein disease with a high risk of progression, which can complicate the rest of your life.
SUBSEQUENT TREATMENT:
- Q switch laser therapy,
- IPL laser therapy,
- local drug treatment.
TROPHIC ULCER TREATMENT
There are many forms of trophic ulcers (they are also called chronic wounds) and they are caused by various reasons. The most common ones can be divided into three large groups – venous, arterial, and neuropathic.
Th. A consultation of a vascular surgeon or phlebologist is compulsory. Further treatment is carried out according to doctor’s instructions.
Venous leg ulcers as the most severe manifestation of CVI are often painful, exuding, cause restricted movement and social isolation and worsen the quality of life for about 1-5% of the population. They can also be of ischaemic origin (atherosclerotic blockage of the arteries). Localised in the legs below the knee.
Accurate diagnosis is important, including a consultation of a vascular surgeon (angiosurgeon) in case of an ulcer.
- compression therapy with low-tension compression bandages is a MUST in case of venous insufficiency ulcers;
- wearing compression stockings – special stockings for ulcers;
- drug therapy.